It impossible for any engine to run efficiently without proper lubrication system.So,for safe,efficient and smooth engine operation lubrication system is must. Purposes of the lubricating system are -
1.supplies lubricating oil to all moving parts in the engine.
2.lub oil picks up engine heat and dissipates it through the oil pan.
3.oil fills the clearances between bearings and rotating journals.
4.lub oil forms a seal between piston rings and cylinder walls.
5.oil acts as a cleaning agent.
Lubricating oil is required to have the following properties-
Proper viscosity - high viscosity oil flows too slowly and low viscosity oil has a reduced ability to stay in place - both of them may cause rapid engine wear
viscosity index (VI) - is a measure of how much the viscosity of oil changes with temperature.
viscosity numbers - single-viscosity oil has several grades - winter grade or other than winter grade.
winter grade oils are SAE 0W, SAE 5W, .., SAE 25W
other than winter grade oils are SAE 20, SAE 30, SAE 40, and SAE 50
the higher the number, the thicker the oil.
multiple-viscosity oil - has VI improver added to the oil - keeps the viscosity of oil nearly unchanged
some multi-viscosity oils are SAE 5W-30, SAE 10W-40, SAE 20W-50
resistance to carbon formation and oil oxidation.
corrosion and rust inhibitors.
detergent-dispersant's.
extreme pressure resistance.
energy-conserving oil - has friction modifiers - a chemical dissolved completely in oil or suspended carbon or molybdenum.
two types of EC oils are EC I and EC II - EC II provides better fuel-economy than an EC I oil
synthetic oil - made from carbon compounds and alcohols, or from coal and crude oil - better than petroleum based oils.
Lubrication system components:
Oil pump - two types of oil pumps are used.
gear-type pump
rotor-type pump
Drive arrangement of oil pumps are:
in
camshaft-in-block engines, the camshaft spiral gear that drives the ignition distributor usually drives the oil pump.
in
OHC engines, the oil pump is driven by separate drive shaft - 'jackshaft'.
in
distributor less engines, oil pumps are driven by crankshaft.
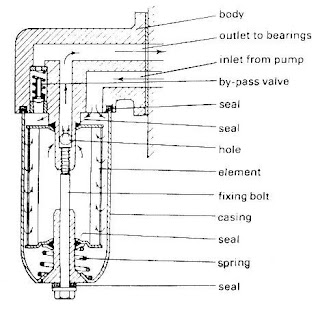
Oil filters:
oil from the pump flows through the filter.the filter has a pleated paper filtering element.it has a spring-loaded bypass valve.some have anti-drain back valve - helps prevent oil from draining out while the engine is off.
some engines use internal oil filters - attach directly to the oil pump.
Oil pressure indicators: warn the driver if engine pressure is too low.There are four types-
indicator light - connected through an oil pressure switch - very common.
el
electric gauge - balancing coil type - the engine unit has a diaphragm connected to a sliding contact.
electronic gauge - bar graph display made up of a series of segments.
Oil level indicator (dipstick):
markings on the dipstick indicate full or add oil.some vehicles have low oil-level indicator light.Some cars have oil-change indicator light -the body control module (BCM) monitors the coolant-temperature sensor, engine speed sensor, and vehicle speed sensor.
Crankcase ventilation:
Crankcase ventilation is necessary to remove water, gasoline, and blow by gases - prevents the formation of sludge.Most recent engines use
positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system.Sludge is a thick, creamy, black substance - clogs oil screen and line.Whipping of water and oil by crankshaft creates sludge, dirt and carbon makes the colour black. Water comes into the crankcase with blow by gases and the crankcase ventilation system.Sludge forms when the engine operates cold most of the time.It forms when the cooling-system thermostat is removed.The vehicle must be driven long enough to prevent sludge
The 'normal operating temperature' vapourises water and blown away by crankcase ventilation system - thus prevents the formation of sludge.In addition to oil, other lubricants and special fluids are used in cars.Grease - a semi-solid fluid is very common made from petroleum and thickened with metallic soaps such as, Li, Ca, Na, Al, and Ba or non-metallic substance like clay .a good grease must have consistency, stability, oxidation resistance, ability to protect against friction, wear and corrosion, and feed ability.they may be-
1.wheel-bearing grease.
2.universal-joint grease.
3.chassis grease.
4.extended-lubrication interval (ELI) chassis grease.
5.multipurpose grease.
6.extreme pressure (EP) grease.
others
The engine loses oil by burning or by leaking.Three main factors resulting in 'more than normal' oil consumption are-
engine speed - high speed produces high temperature and lowers oil viscosity - oil can get into the combustion chamber and get burnt, oil-control ring can flutter or float, crankcase ventilation system takes some oil with it in the form of mist.
engine wear - such as, bearing wear, cylinder wear, piston ring wear, valve guide wear - causes more oil consumption.
engine oil can leak past the gaskets (sealing), from loose fittings, or filter
Causes of low oil pressure are:
1.A weak or broken relief valve spring.
2.A worn oil pump .
3.A broken or cracked oil line.
4.An obstruction in the oil line.
5.Insufficient or thin oil.
6.Worn engine bearings.
7.A leaking oil filter, oil filter gasket, or oil-pressure sending unit.
Excessive oil pressure results from-
1. A stuck pressure relief valve.
2.Wrong spring in the pressure relief valve.
3.A clogged oil line.
4.Thick oil.
Oil changes:
Change oil when it gets dirty or contaminated - a result of wearing out of additives
- schedule I - change engine oil and filter every 5000 km
- schedule II - change oil every 12,500 km and change the oil filter the first oil change and every other time after that